SMC Technology
SMC (Sheet Moulding Compound) – pre-impregnated with thermosetting resins, thickened, glass-filled compound.
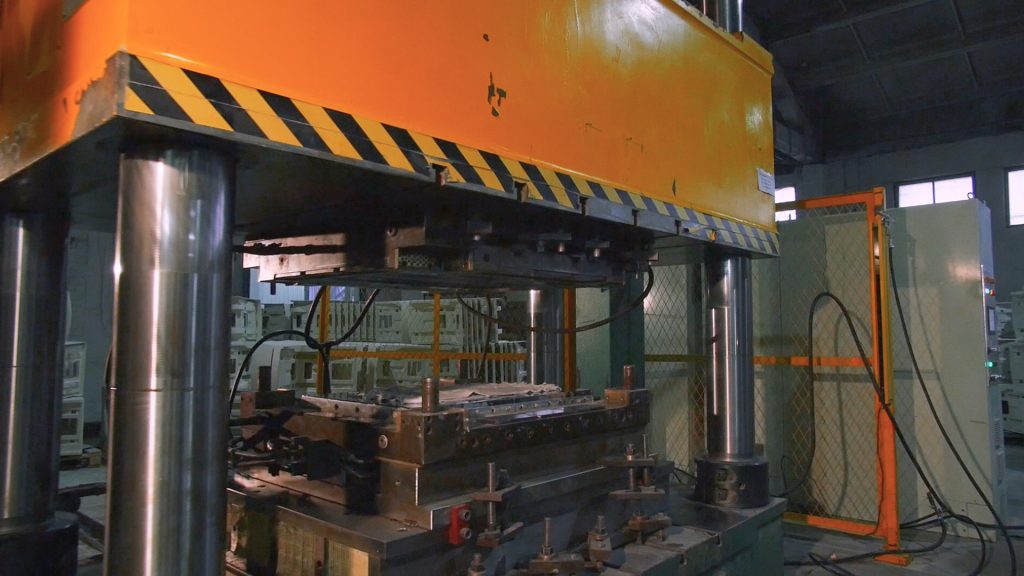
The method of direct hot pressing from flowable prepregs (SMC technology) allows to produce products of complex geometry in medium and large series (from 10,000 products per year). The starting material is SMC prepreg – fibrous press material.
Prepreg is processed into final products in automatic hydraulic presses.
This technology is an advanced and highly productive way of manufacturing parts from polymer fiber composites.
The cycle of manufacturing the parts on average does not exceed five minutes. At the same time, products with high surface quality are obtained, which are uniform in volume (without air inclusions and defects).

Advantages of this technology
The whole group of SMC prepregs (flowable prepregs) has a number of properties that sharply distinguish them from other structural materials.
Due to its high mechanical characteristics over a wide range of temperatures, excellent corrosion resistance, low cost, SMC can effectively replace traditional materials in various industries.
- increased accuracy (low tolerances), almost no additional processing is required
- fast fabrication (can be used for mass production)
- lightly colored surface (up to class A)
- wear resistance of the surface, low porosity
- The highest quality of the resulting surface and excellent appearance
- products do not burn out in the sun and are frost-resistant
- low (almost zero) shrinkage
- high thermal and corrosion resistance
- chemical resistance
- low energy consumption in production
- low emissions in production
- low weight
- low operating costs
- long service life
- possibility of recycling
- high strength properties
- high curing speed
- Low cost with a large volume of production.
SMC technology is used in the manufacture of products for which the main characteristics are mechanical strength and high surface quality in combination with the ease of the material.
Scope of products from SMC:
- Automotive;
- Electrical engineering;
- Rail transport;
- Water transport;
- Construction and communication architecture;
- Plumbing;
- Sports facilities, tools and other applications.



